How do students learn thousands of new words each year?

Did you know that hundreds of new words such as selfie, hangry, binge-watch, cray, and SMH (shake my head!) are added to the Oxford English dictionary every year?
Students must learn thousands of new words each year, to be able to communicate effectively socially, and at school.
In fact, by the time a person leaves school they will have more than 20,000 words in their personal vocabulary.
How do we learn new words?
The ability to learn vocabulary is linked to our background knowledge, and new words are easier to learn when we can connect them to our existing vocabulary. For example, if you know the word bright it is quite easy to learn the word luminous.
Words are more difficult to learn when we don’t understand the meaning of the word. For example, if you are studying history and come across the word, suffragette, you may not have sufficient background knowledge to really understand its meaning.
Which words to teach?
With more than 170,000 words in the English language, how do teachers decide which words to teach?
Vocabulary can be sorted into tiers based on how frequently they are used, and how complex they are. Teachers use this model to prioritise the words to they teach to students.
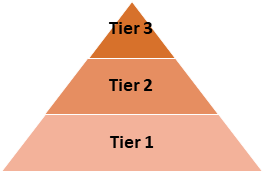 Tier 1 words are everyday words used in conversation, such as girl, walk and happy. Teachers do not usually need to teach the meaning of these words.
Tier 1 words are everyday words used in conversation, such as girl, walk and happy. Teachers do not usually need to teach the meaning of these words.
Tier 2 words express complex ideas, in a range of content areas, such as season, analyse and endangered. These words are usually taught explicitly.
Tier 3 words are specific words needed in specialised subjects, such as molecule, gigabyte and pulmonary. These words are taught as the need arises.
Vocabulary strategies
There are four strategies that we can use to help students build their vocabulary:
Meaning
Show students how new words relate to each other, and to the words they already know.
Strategies to teach meaning include:
• Word walls
• Word webs
• Homophone and homonym activities
• Synonym and antonym activities
Sounds
Build students phonemic awareness by showing them how to identify individual sounds in words, and match speech sounds with letter patterns. Develop their phonological awareness by showing students how to break words into syllables.
Strategies to teach phonological awareness include:
• Syllable activities
• Rhyming games
• Following the beat activities
Word parts
Show students how words are formed from basic root words, and how the meaning of words can be changed by adding prefixes and suffixes.
Strategies to teach word parts include:
• Creating word families
• Building words from root words
• Activities using prefixes and suffixes
Word order
Show students how syntax, which is the order of words, changes the meaning of sentences, such as “I can fly! “and “Can I fly?”
Strategies to teach word order include:
• Modelling correct grammar
• Sentence structure, verb tenses, punctuation other grammar activities
• Chunking sentences
Our video: Helping Students Build Their Vocabulary demonstrates how to build students vocabulary through meaning, sounds, word parts and word types. Here is a preview of three practical vocabulary strategies that will get you started.


